Practice Midterm
Try taking this practice test without looking at the answers. These questions are similar to what will be on the midterm.
Bit
Question 1
What image will the following code draw?
from byubit import Bit
def turn(bit):
bit.left()
bit.move()
bit.left()
@Bit.empty_world(5, 3)
def run(bit):
while bit.front_clear():
bit.move()
bit.paint('green')
turn(bit)
while bit.front_clear():
bit.move()
bit.paint('blue')
if __name__ == '__main__':
run(Bit.new_bit)a.
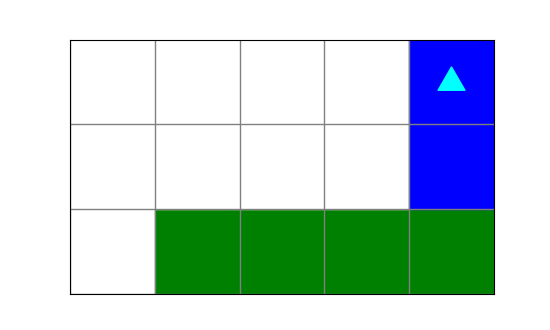
b.
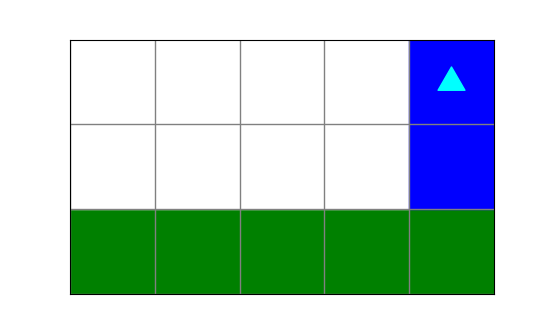
c.
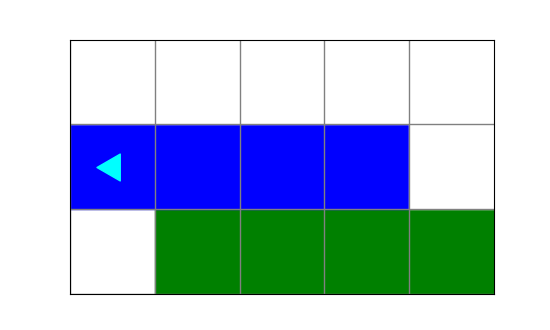
d.
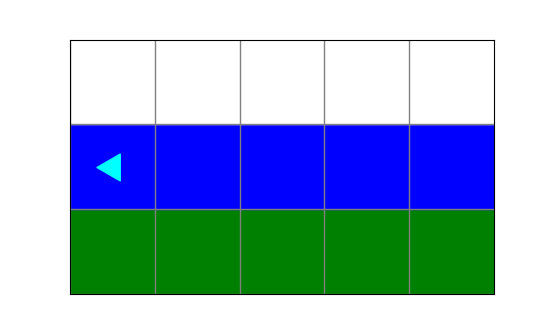
Question 2
You are given this code:
from byubit import Bit
def turn(bit):
bit.left()
bit.move()
bit.left()
def change(bit):
if bit.is_red():
bit.paint('green')
if bit.is_blue():
bit.paint('red')
def do_change(bit):
while bit.front_clear():
bit.move()
change(bit)
if __name__ == '__main__':
run(Bit.new_bit)And you have this starting world:
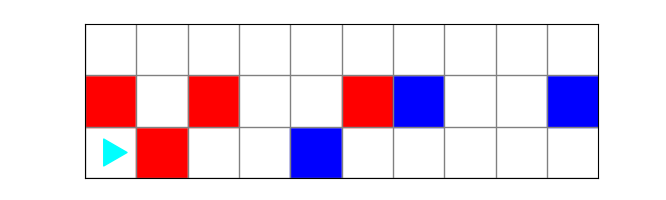
and this desired finishing world:
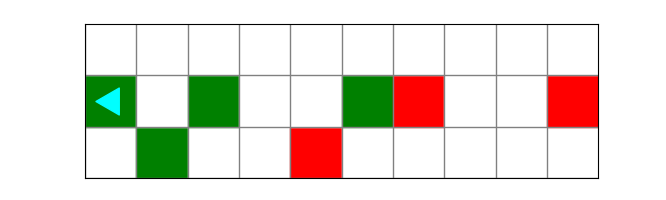
Carefully draw out the result of each code block. Which block of code will produce the correct ending world?
a.
@Bit.worlds('start')
def run(bit):
turn(bit)
do_change(bit)
turn(bit)
do_change(bit)b.
@Bit.worlds('start')
def run(bit):
do_change(bit)
turn(bit)
change(bit)
do_change(bit)c.
@Bit.worlds('start')
def run(bit):
do_change(bit)
do_change(bit)d.
@Bit.worlds('start')
def run(bit):
do_change(bit)
turn(bit)
do_change(bit)Question 3
The coyote is stuck and needs to get back on the cliff. You have this starting world:

and this finishing world:
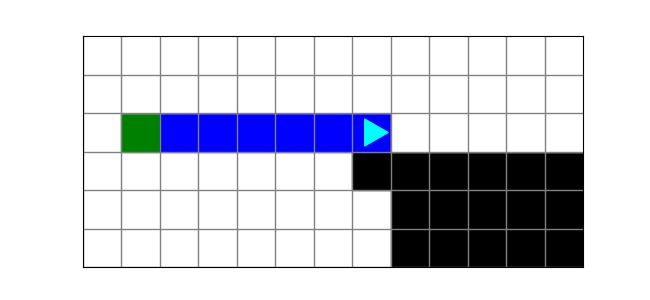
You are given this code:
from byubit import Bit
if __name__ == '__main__':
run(Bit.new_bit)Which block of code produces the correct finishing world?
a.
@Bit.worlds('cliff')
def run(bit):
bit.paint('blue')
while bit.right_clear():
bit.move()
bit.paint('blue')b.
@Bit.worlds('cliff')
def run(bit):
bit.paint('green')
while bit.right_clear():
bit.paint('blue')
bit.move()c.
@Bit.worlds('cliff')
def run(bit):
bit.paint('green')
while not bit.right_clear():
bit.move()
bit.paint('blue')d.
@Bit.worlds('cliff')
def run(bit):
bit.paint('green')
while bit.right_clear():
bit.move()
bit.paint('blue')Question 4
What does this code create?
from byubit import Bit
def paint_and_turn(bit, color):
bit.paint(color)
bit.left()
bit.move()
bit.left()
@Bit.empty_world(8, 8)
def run(bit):
while not bit.is_blue():
bit.paint('blue')
bit.move()
if not bit.front_clear():
paint_and_turn(bit, 'blue')
if __name__ == '__main__':
run(Bit.new_bit)a.
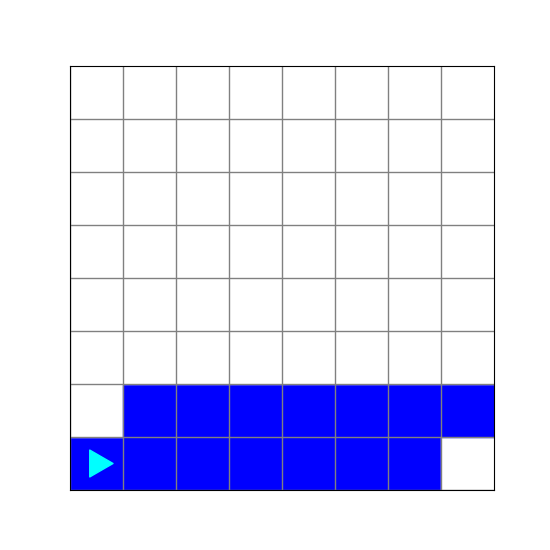
b.
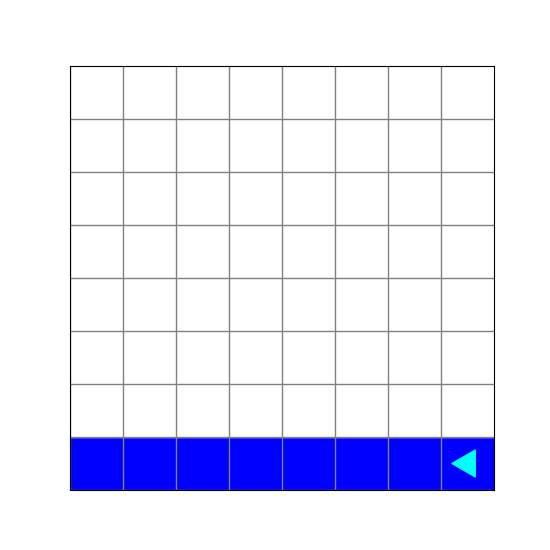
c.
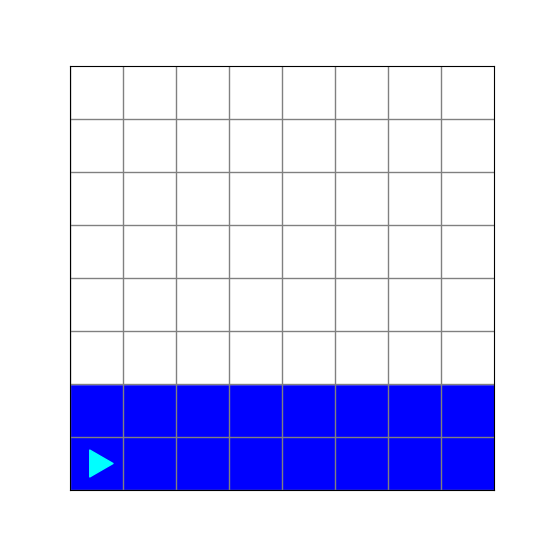
d.
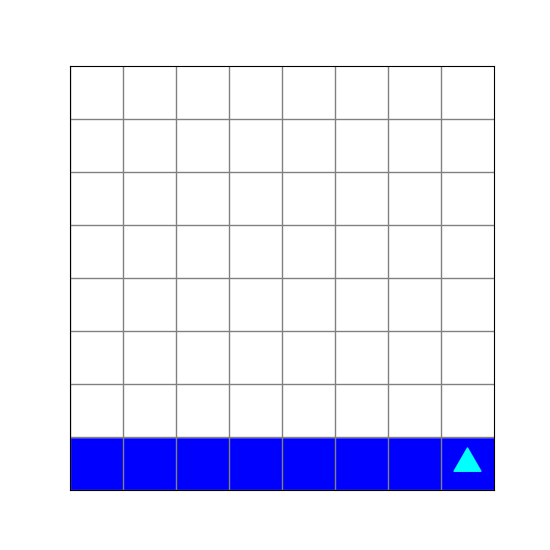
Input Loops
Question 5
Which block of code could produce the following dialog?
Rock, paper, or scissors? rock
I have rock: but mine is bigger, you lose
Rock, paper, or scissors? scissors
I have rock: you lose, try again
Rock, paper, or scissors? paper
I have scissors: your paper is shredded, you lose, try again
Rock, paper, or scissors? bomb
You win, my rock can't beat a bombwinner_of_round() is called within game().
def game():
winner = winner_of_round()
while winner != "You":
winner = winner_of_round()Check all that apply.
a.
def winner_of_round():
response = input('Rock, paper, or scissors? ')
if response == 'rock':
print('I have rock: but mine is bigger, you lose')
if response == 'scissors':
print('I have rock: you lose, try again')
if response == 'paper':
print('I have scissors: your paper is shredded, you lose, try again')
print(f"You win, my rock can't beat a {response}")
return "You"b.
def winner_of_round():
response = input('Rock, paper, or scissors? ')
if response == 'rock':
print('I have rock: but mine is bigger, you lose')
elif response == 'scissors':
print('I have rock: you lose, try again')
elif response == 'paper':
print('I have scissors: your paper is shredded, you lose, try again')
else:
print(f"You win, my rock can't beat a {response}")
return "You"c.
def winner_of_round():
response = input('Rock, paper, or scissors? ')
if response == 'rock':
print('I have rock: but mine is bigger, you lose')
return "Me"
if response == 'scissors':
print('I have rock: you lose, try again')
return "Me"
if response == 'paper':
print('I have scissors: your paper is shredded, you lose, try again')
return "Me"
print(f"You win, my rock can't beat a {response}")
return "You"d.
def winner_of_round():
response = input('Rock, paper, or scissors? ')
if response != 'rock' and response != 'paper' and response != 'scissors':
print(f"You win, my rock can't beat a {response}")
return "You"
if response == 'rock':
print('I have rock: but mine is bigger, you lose')
return "Me"
if response == 'scissors':
print('I have rock: you lose, try again')
return "Me"
print('I have scissors: your paper is shredded, you lose, try again')
return "Me"Question 6
Which of the following dialogs is possible with this code?
def get_books():
books = []
while True:
book = input('What book do you want to read? ')
if book == '':
break
if book == "My Favorite Recipes, by Dr. Page":
print('We will put you on the waitlist!')
books.append(book)
if len(books) == 0:
print("Boo. You should read more")
elif len(books) <= 3:
print("That's a great list of books.")
else:
print("You know you're never going to read all of those")
if __name__ == '__main__':
get_books()a.
What book do you want to read?
That's a great list of books.b.
What book do you want to read? In Search of Lost Time
What book do you want to read? One Hundred Years of Solitude
What book do you want to read? Pride and Prejudice
What book do you want to read? The Grapes of Wrath
What book do you want to read? Beloved
What book do you want to read? Wuthering Heights
You know you're never going to read all of thosec.
What book do you want to read? The Grapes of Wrath
What book do you want to read? Beloved
What book do you want to read? Wuthering Heights
What book do you want to read?
That's a great list of books.d.
What book do you want to read? In Search of Lost Time
What book do you want to read? One Hundred Years of Solitude
What book do you want to read? Pride and Prejudice
What book do you want to read?
You know you're never going to read all of thoseLists
Question 7
Which user-defined functions are executed by Python in the following code?
def less(a, b):
if a < b:
return True
else:
return False
def filter(numbers):
new_list = []
previous = None
for number in numbers:
if previous is None or less(number, previous):
new_list.append(number)
previous = number
return new_list
def add(a, b):
return a + b
if __name__ == '__main__':
some_numbers = [10, 8, 9, 7, 11, 2]
result = filter(some_numbers)
print(result)a. filter()
b. less()
c. less(), filter()
d. less(), filter(), add()
Question 8
In the same code above, what is printed?
a. [10, 8, 9, 7, 11, 2]
b. [8, 7, 2]
c. [10, 8, 7, 2]
d. [10, 8, 9, 7, 2]
Question 9
In the same code above, how many times is less() called?
a. 1
b. 3
c. 5
d. 6
Question 10
What does the following code print?
def filter(numbers, lower, upper):
new_numbers = []
for number in numbers:
if number > lower and number < upper:
new_numbers.append(number)
return new_numbers
def accumulate(numbers):
total = 0
for number in numbers:
total += number
return total / len(numbers)
if __name__ == '__main__':
list1 = [1, 10, 5, 3, 8]
list2 = filter(list1, 2, 8)
print(accumulate(list2))a. 4
b. 2
c. 4.0
d. 2.0
Question 11
Consider the following code:
airports = [
('SLC', 'Salt Lake City', 'Oregon', 'International'),
('IDA', 'Idaho Falls', 'Idaho', 'Regional')
]Which code will loop through a list of airport tuples and unpack them into variables?
a.
for airports in code, city, state, status:
print(f'{city}, {state} ({code}; {status})')b.
for every airport in airports:
print(f'{airport.city}, {airport.state} ({airport.code}; {airport.status})')c.
while True:
print(f'{city}, {state} ({code}; {status})')d.
for code, city, state, status in airports:
print(f'{city}, {state} ({code}; {status})')Question 12
Write an example for each of the following list patterns:
- mapping
- filter
- selection
- accumulate
Question 13
def get_details():
subject = input('Subject: ')
seconds = float(input('Seconds observed: '))
location = input('Location: ')
score = float(input('Clarity score (0-1): '))
if subject == '' or location == '' or seconds < 2 or score < 0.3:
return None
return (subject, seconds, location, score)Select all of the following inputs that would cause get_details to return
None:
a.
Subject: Big Foot
Seconds observed: 2.5
Location: Alberta
Clarity score (0-1): 0.3b.
Subject: Cosmo
Seconds observed: 7
Location: Y Mountain
Clarity score (0-1): 0.1c.
Subject:
Seconds observed: 10
Location: Wilkinson Center
Clarity score (0-1): 1d.
Subject: Yetti
Seconds observed: 0.5
Location: Timpanogos
Clarity score (0-1): 0.9Question 14
What does the following code print?
def filter_north(deliveries):
filtered = []
for name, house_number in deliveries:
if house_number % 2 == 0:
filtered.append(house_number)
return filtered
def filter_south(deliveries):
filtered = []
for name, house_number in deliveries:
if house_number % 2 == 1:
filtered.append(house_number)
return filtered
def main(deliveries):
northside = len(filter_north(deliveries))
southside = len(filter_south(deliveries))
if northside > southside:
print(f'North > south, with {northside} deliveries.')
elif southside > northside:
print(f'South > north, with {southside} deliveries.')
else:
print(f'Both sides have {northside} deliveries.')
if __name__ == '__main__':
deliveries_pine_street = [('Adam', 1010),
('Sarah', 1011),
('David', 1028),
('Peter', 1041),
('Joseph', 1043)]
main(deliveries_pine_street)
a. Both sides have 3 deliveries.
b. South > north, with 3 deliveries.
c. North > south, with 4 deliveries.
d. Sorth > north, with 4 deliveries.
Question 15
You need to write a function that gets a valid class rating, from 1 to 10. If a rating is less than 1 or greater than 10, then say the rating is not valid and ask again for a rating. Otherwise, return the valid rating.
Which of these functions accomplishes this?
a.
def get_valid_rating():
while True:
rating = input('Rating: ')
if rating < '1' or rating > '10':
print('Sorry, that is not a valid rating.')
else:
return ratingb.
def get_valid_rating():
while True:
rating = int(input('Rating: '))
if rating < 1 or rating > 10:
print('Sorry, that is not a valid rating.')
return ratingc.
def get_valid_rating():
while True:
rating = int(input('Rating: '))
if rating < 1 or rating > 10:
print('Sorry, that is not a valid rating.')
else:
return ratingd.
def get_valid_rating():
while True:
rating = int(input('Rating: '))
if rating >= 1 or rating <= 10:
return rating
else:
print('Sorry, that is not a valid rating.')Question 16
You need to write code that gets information about fruit for sale in a store.
Each fruit has a name, number of days it will stay fresh, and a price. The days
can never be less than 3 or greater than 10. The price can never be less than
0.1 or greater than 5.50. If any data is not valid, the function returns
None.
Which of these functions accomplishes this?
a.
def get_fruit_info():
name = input('Name: ')
days = int(input('Days: '))
price = float(input('Price: '))
if days < 3 or days > 10:
if price < 0.1 or price > 5.50:
return None
return name, days, priceb.
def get_fruit_info():
name = input('Name: ')
days = int(input('Days: '))
price = float(input('Price: '))
if days >= 3 or days <= 10:
return name, days, price
if price >= 0.1 or price <= 5.50:
return name, days, price
return Nonec.
def get_fruit_info():
name = input('Name: ')
days = int(input('Days: '))
price = float(input('Price: '))
if days < 3 or days > 10:
return None
if price > 0.1 or price < 5.50:
return None
return name, days, priced.
def get_fruit_info():
name = input('Name: ')
days = int(input('Days: '))
price = float(input('Price: '))
if days < 3 or days > 10:
return None
if price < 0.1 or price > 5.50:
return None
return name, days, price